There have been a few questions about how palm scanners work, and how this affects reliability. Let’s take a look at the technology, its strengths, and its weaknesses.
If you’ve ever had a pulse ox on your finger, you know that it is a system that allows a machine to determine how much oxygen is in your blood. Have you ever asked yourself how it works?
Hemoglobin in the human body is responsible for transporting oxygen. Deoxidized hemoglobin absorbs infrared light differently than does oxidized hemoglobin. The pulse ox shines two different frequencies of near infrared light through your skin, and measures how much of the different wavelengths gets absorbed, and uses this to calculate the ratio of oxidized to deoxidized hemoglobin in your blood. Palm scanners use the same technology to determine your identity.
Veins transport deoxygenated blood to the heart. Therefore hemoglobin present in vein blood is deoxidized. When the near-infrared light from the palm scanner is directed on a person’s palm, hemoglobin absorbs its rays. The veins’ capacity to reflect the light is reduced, and they appear like a black pattern on the image taken by the system. Then the system processes the image and compares the results with the data from the database.
Since the pattern of veins in the palm is unique to each person, this image is a very accurate way of verifying that the person who was just scanned is the same person who has been scanned in the past. All you have to do is verify a person’s identity at the same time that you scan their palm and place the image in the database. Future scans verify that the person scanned in the future is the same person who was scanned and identified in the past.
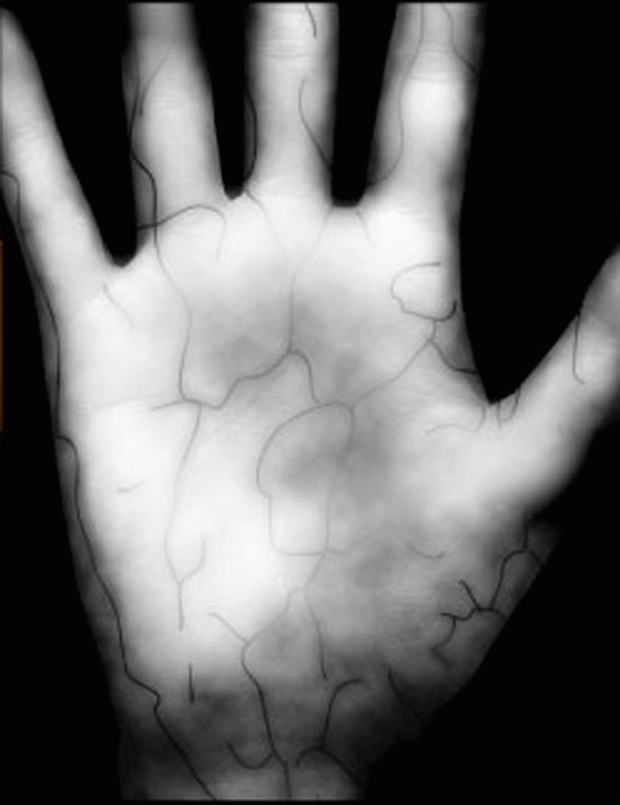
Strengths:
- Given the possibilities of modern technology, many biometric identifiers, like face or voice patterns, can easily become subject to forgery. Palm vein patterns are hidden inside the human’s body and are more difficult to capture without a person’s knowledge.
- Unlike the face, which is visible to anyone in a public place, palm vein patterns cannot be scanned from a distance without a person’s consent.
- The palm vein pattern is significantly bigger in size than those of the finger or iris. Consequently, the scan from it contains more data, which increases the accuracy of the identification.
- Unlike many other biometric parameters (face, fingerprints), palm vein patterns are not likely to change due to some unexpected circumstances over the course of a person’s life.
- The technique of identifying a person by their fingerprints has a number of serious disadvantages. Fingerprints are easily affected by external factors, like aging, disease, or the state of the skin on the hands. Palm vein patterns usually remain the same throughout the person’s life.
- The results of the measurement are not affected by the state of the hand’s surface: dirt, grease, and oil don’t affect the image because IR passes through these substances easily.
- Unlike retina scans, the risk of passing infections is lower because the system doesn’t require physical contact.
Weaknesses:
- Some health factors, such as fevers, can affect the quality of the image
- Companies aren’t always great about information security when storing their database, but this is true of all identification technologies
Palm scanners have been in use by the medical field for identification purposes for over a decade. Banks in Japan have been using it for even longer.